Nerve Biopsy
A nerve biopsy is a procedure in which a sample of nerve tissue is removed from the body and examined in the laboratory. A nerve biopsy may be necessary to help diagnose the diseases of the nerves, also called neuropathy. Sensory nerves (nerves that transfer sensations like cold, heat or pain to the brain) are commonly subjected to biopsy. Other nerves are rarely biopsied.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) for Epilepsy
The vagus nerve is responsible for involuntary functions such as control of the body’s heart rate and digestive tract. The nerve runs from the lower part of the brain, through the neck, to various organs in the chest and abdomen, on both sides of your body. Damage or compression of the vagus nerve can lead to many conditions. Stimulation of the vagus nerve has been suggested in the treatment of depression and epilepsy, especially partial seizures (limited to a part of the brain) when medications have failed.
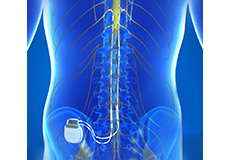
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
Peripheral nerve stimulation is a minimally invasive treatment for chronic pain and pain caused due to peripheral nerve damage. The peripheral nerves connect your brain and spinal cord with the rest of the body. Pain arises from the signals produced by a nerve when it is stimulated by tissue damage or when the nerve itself is damaged (neuropathic pain). Peripheral nerve stimulation involves stimulation of the affected nerves using electrical impulses generated by a device implanted in your body. This interrupts the transmission of pain signals so that, instead of pain, you experience a mild tingling.
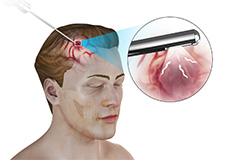
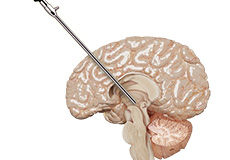
Endoscopic Brain Surgery
Endoscopic brain surgery, also known as endoscopic cranial surgery, is a minimally invasive procedure to identify and treat abnormal conditions deep within the brain. The procedure may be performed through one or two small incisions on the skull or another opening of your body such as the nostrils.
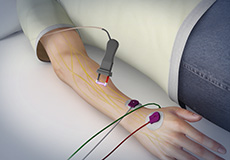
EMG and Nerve Conduction Studies
An electromyogram (EMG) is a medical test performed to measure the electrical activity of muscles in the body. Nerve conduction studies measure how well and how fast nerves send electrical signals to the muscles. EMG and nerve conduction studies are often done together to provide more in-depth information to the physician.
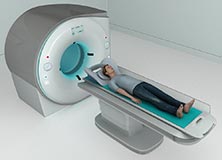
Head CT Scan
Computerized tomography (CT) scan is an imaging technique that uses a combination of a special X-ray machine and a computer to obtain cross-sectional images of the internal structures of the body. A contrast material or dye may be injected into a specific part of your body to obtain a more detailed view. The images obtained are used to diagnose a variety of diseases. A CT scan is also called Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT) scan. Head CT scan is used to obtain pictures of the skull, brain, blood vessels (head), sinuses, etc.
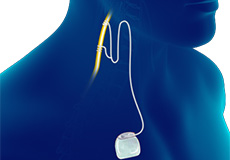
Vagal Nerve Stimulator Placement & Battery Exchanges
Vagal nerve stimulator (VNS) placement and battery exchanges refer to a minimally invasive procedure in which a pulse generator device similar to a pacemaker is inserted in your neck to treat certain forms of epilepsy (seizure disorder) and depression.
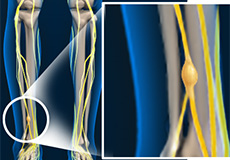
Peripheral Neuropathy
The peripheral nervous system transmits signals from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Any disruption in the normal functioning of the peripheral nervous system can result in numbness, pain, and weakness in your hands and feet as well as other parts of your body. Peripheral nerves are fragile and easily damaged. A nerve injury can affect your brain's ability to communicate with your muscles and organs. Damage to the peripheral nerves is called peripheral neuropathy.
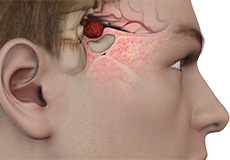
Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths within the pituitary gland, a small gland located near the base of the brain. Pituitary tumors can be either functioning or non-functioning. Functioning tumors secrete pituitary hormones that can lead to a clinical syndrome, while non-functioning tumors are those that can cause a syndrome by not secreting pituitary hormones.
Multiple Sclerosis and Pain
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) affecting the myelin sheath which insulates nerve cells and is important for the transmission of nerve impulses. This causes the relay of information between the brain and the rest of your body to either slow down or stop and can lead to muscle weakness, difficulty with coordination and balance, vision and speech difficulties, tremors, dizziness, and cognitive difficulties.
Myopathy
Myopathy is a group of neuromuscular disorders, characterized by muscle weakness and dysfunction of muscle fibers, caused by abnormalities in the structure and metabolism of muscle cells. Myopathy may be associated with inflammatory conditions, endocrine and infectious diseases, drugs or toxic causes. There are many types of myopathies and they may be either acquired (such as muscle cramps) or inherited (muscular dystrophy).
Seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief attack caused by changes in the brain’s electrical activity. It is quite common in people with a brain tumor. During a seizure, a person’s brain cells misfire, releasing electrical energy in an uncontrolled manner. This results in a sudden buildup of energy through the brain, causing unconsciousness and contractions of the muscles. The person may cry, become unconscious, or twitch involuntarily.
Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic brain injuries occur when a sudden trauma, such as a violent blow or jolt to the head, causes brain damage.
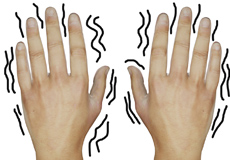
Tremor
A tremor is an involuntary muscle movement characterized by shaking of a body part, usually the hands and arms, and difficulty holding and controlling objects. It may also involve other parts of the body such as the vocal cords and head. A slight tremor is normally present in all of us, especially the elderly. It increases when we are angry, fearful, under stress, fatigued, smoke, drink a lot of caffeine or as a response to certain medications.
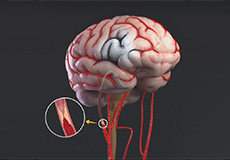
Stroke
The brain requires a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients from the blood in order to function properly. A blockage, interruption or severe reduction in the supply of blood to the brain can result in a condition called a stroke. Stroke is a medical emergency that leads to the death of brain cells within minutes of the interruption in blood supply. Prompt treatment is vital to minimize brain damage and improve outcomes. Stroke is more common in men over 55 and African Americans.
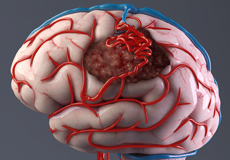
Vascular Brain Tumor
A vascular brain tumor is caused due to an abnormal growth of the blood vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord and is non-cancerous (benign). It commonly occurs at the cerebellum, which is present at the back of your head and helps to maintain your body’s balance.
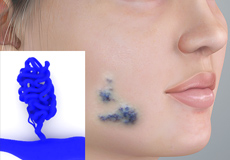
Venous Malformation
Venous malformations (VMs) are non-cancerous growths caused due to abnormal development of the veins. They are commonly seen on the surface of the skin as a soft bluish discoloration but can also develop in the joints, muscles, gastrointestinal tract and other internal organs.
Peripheral Nerve Conditions
Peripheral nerve conditions are disorders caused by malfunctioning of the nerves due to peripheral nerve damage or destruction. The peripheral nervous system sends signals from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of your body. Any disruption in the normal functioning of the peripheral nervous system can result in numbness, pain, and weakness in your hands and feet as well as other parts of your body.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition characterized by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in and around the brain, which causes swelling of the brain and affects normal brain function.
Restless Leg Syndrome
Restless leg syndrome (RLS), also known as the Willis-Ekbom disease, is a neurological sleep disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs. The condition interferes with your sleep, making it difficult to fall asleep.
Headache Basics
Pain in any region of the head is called a headache. It may involve one or both sides of the head and may radiate to the neck and shoulders. You may experience dull pressure, a throbbing sensation or sharp pain that may last anywhere between an hour to days. In some cases, it may indicate a serious underlying disease.
Anatomy of the Brain
The human brain is a three-pound organ and is located within the skull. It is the most complex and one of the largest organs in the human body and plays a major role in almost all body functions. It controls speech, memory, thoughts, leg and arm movements, as well as the function of several organs within the body. It also regulates the secretion of hormones and breathing and heart rates.